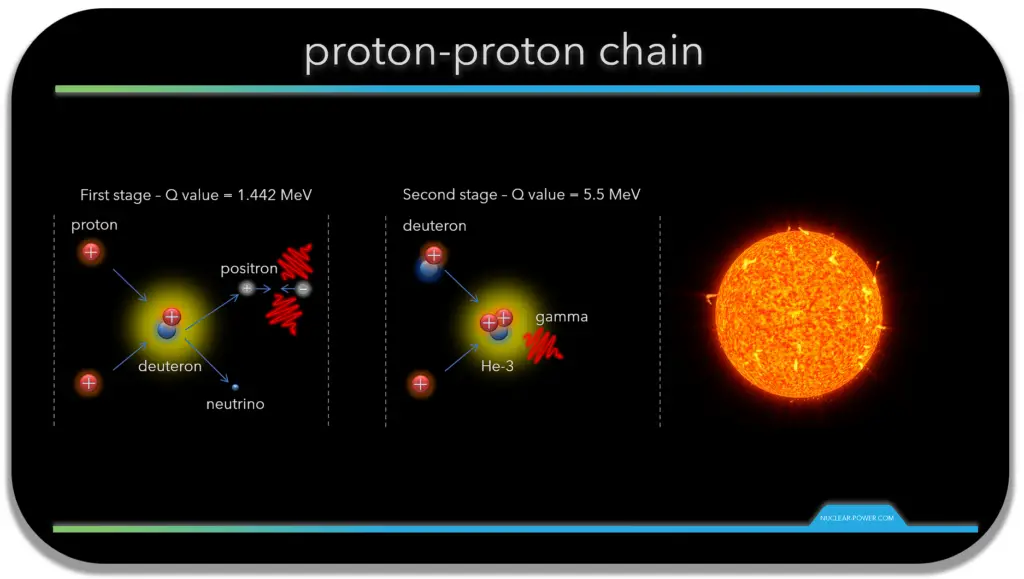
The proton-proton chain is a series of nuclear fusion reactions that occur in the core of stars like the Sun. It is the primary source of energy for stars with masses similar to or smaller than the Sun.
The Process
The proton-proton chain involves the fusion of hydrogen nuclei (protons) to form helium nuclei. The process occurs in several steps:
- Two protons fuse to form deuterium: This step releases a positron (a positively charged electron) and a neutrino.
- Deuterium fuses with a proton to form helium-3: This step releases a gamma ray.
- Two helium-3 nuclei fuse to form helium-4: This step releases two protons.
The net result of these reactions is the conversion of four hydrogen nuclei into one helium nucleus, releasing energy in the form of gamma rays, positrons, and neutrinos.
Significance of the Proton-Proton Chain
- Solar Energy: The proton-proton chain is responsible for the vast majority of the energy produced by the Sun. This energy is radiated into space as sunlight and heat.
- Stellar Evolution: The proton-proton chain is a key factor in the evolution of stars. As stars consume hydrogen and produce helium, their internal structure and energy output change.
- Neutrino Production: The proton-proton chain produces a large number of neutrinos, which are subatomic particles that can pass through matter with little interaction. The study of neutrinos from the Sun has helped scientists understand the processes occurring within its core.
Would you like to learn more about other types of nuclear fusion reactions or the role of the proton-proton chain in the evolution of stars?