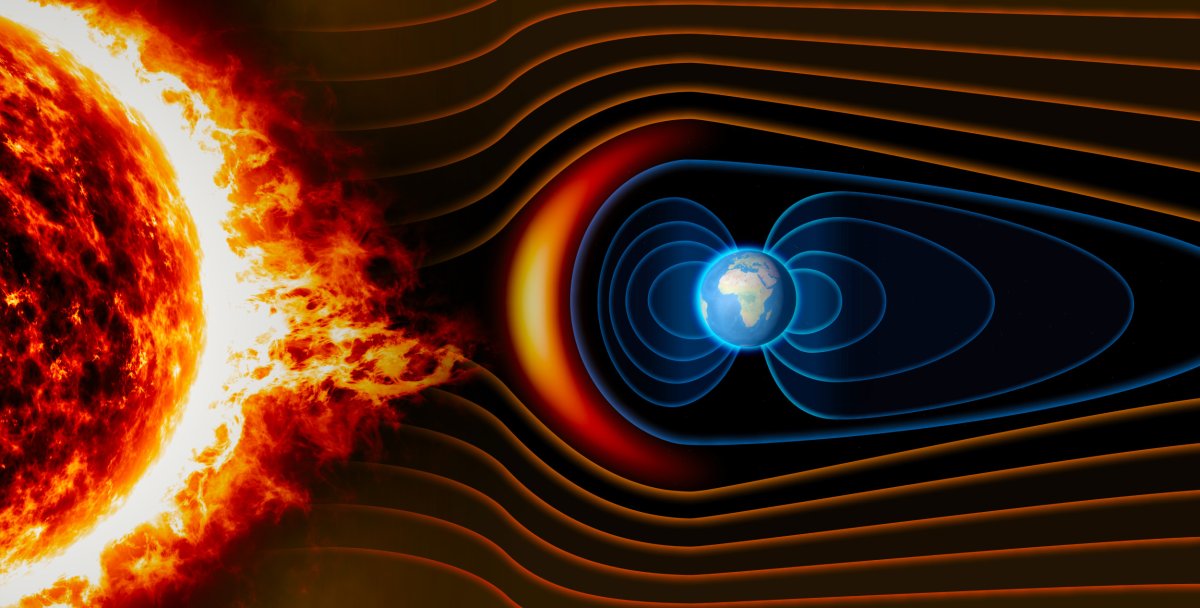
Geomagnetic storms are disturbances in Earth’s magnetic field caused by the interaction of solar wind and the magnetosphere. These storms can have significant impacts on technology and infrastructure, as well as on the environment.
Causes of Geomagnetic Storms
- Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs): Massive clouds of plasma and magnetic field lines ejected from the Sun can interact with Earth’s magnetic field, causing geomagnetic storms.
- High-Speed Solar Wind: Fast-moving streams of solar wind can also trigger geomagnetic storms.
Effects of Geomagnetic Storms
- Disruption of Technology: Geomagnetic storms can disrupt power grids, satellites, and communication systems. This can lead to blackouts, interruptions in services, and financial losses.
- Auroras: Geomagnetic storms can produce stunning displays of light known as auroras, which are visible in high-latitude regions.
- Radiation Hazards: Geomagnetic storms can increase the amount of radiation reaching Earth’s surface, which can pose a risk to astronauts and spacecraft.
Predicting and Mitigating Geomagnetic Storms
- Space Weather Forecasting: Scientists constantly monitor the Sun for signs of solar activity and use models to predict the potential impacts of geomagnetic storms.
- Infrastructure Protection: Utilities and other industries can take steps to protect their infrastructure from the effects of geomagnetic storms.
- Early Warning Systems: Early warning systems can help to alert operators of potential disruptions.
Geomagnetic storms are a natural phenomenon that can have significant impacts on Earth. By understanding the causes and effects of these storms, we can better prepare for and mitigate their consequences.
Would you like to learn more about a specific aspect of geomagnetic storms, such as their causes, effects, or how to prepare for them?