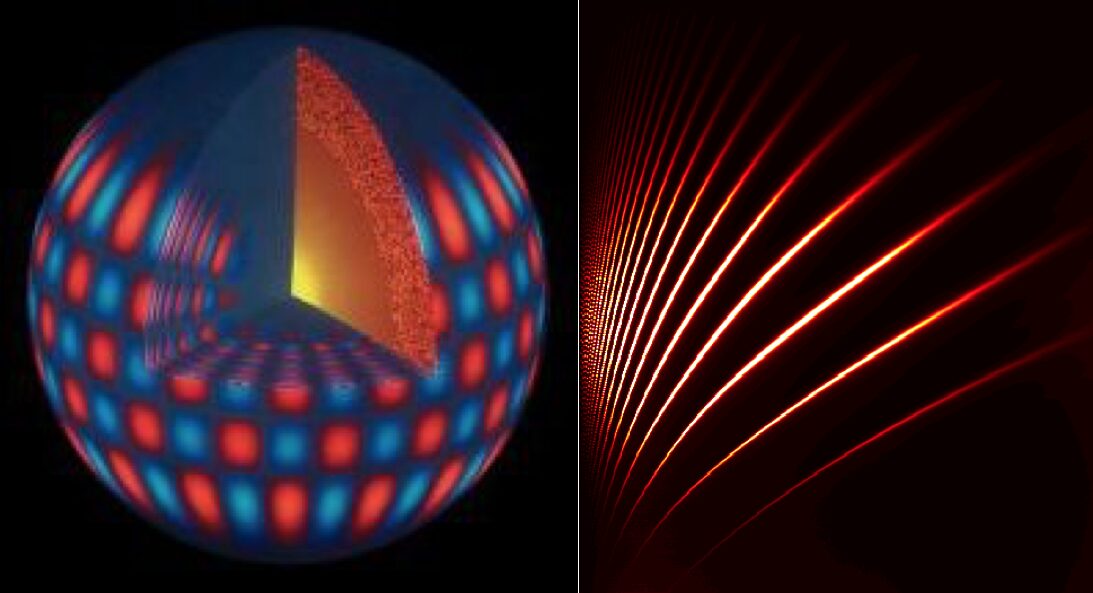
Helioseismology is the study of the sun’s interior using the vibrations or oscillations of its surface. Just as seismologists use earthquakes to study the Earth’s interior, helioseismologists use the sun’s vibrations to probe its structure and dynamics.
How Does Helioseismology Work?
- Solar Oscillations: The sun’s surface is constantly rippling with millions of tiny oscillations. These oscillations are caused by sound waves that travel through the sun’s interior and emerge at the surface.
- Observing Oscillations: Helioseismologists use specialized telescopes to measure the Doppler shift of the sun’s surface, which reveals the motion of the oscillations.
- Inferring Interior Structure: By analyzing the patterns of these oscillations, scientists can infer information about the sun’s temperature, density, and composition at different depths.
Key Discoveries from Helioseismology
Helioseismology has revolutionized our understanding of the sun. Some of its key discoveries include:
- Solar Rotation: Helioseismology has revealed that the sun rotates differentially, meaning the equator rotates faster than the poles.
- Convection Zone: Helioseismologists have mapped the extent of the sun’s convection zone, where hot material rises to the surface and cooler material sinks.
- Solar Neutrinos: Helioseismology has helped to confirm the existence of solar neutrinos, elusive particles produced in the sun’s core.
- Solar Interior Dynamics: Helioseismology has provided insights into the sun’s internal dynamics, such as the transport of energy and the evolution of its magnetic field.
Helioseismology is a powerful tool for studying the sun’s interior and understanding its complex behavior. It continues to play a vital role in solar physics research.