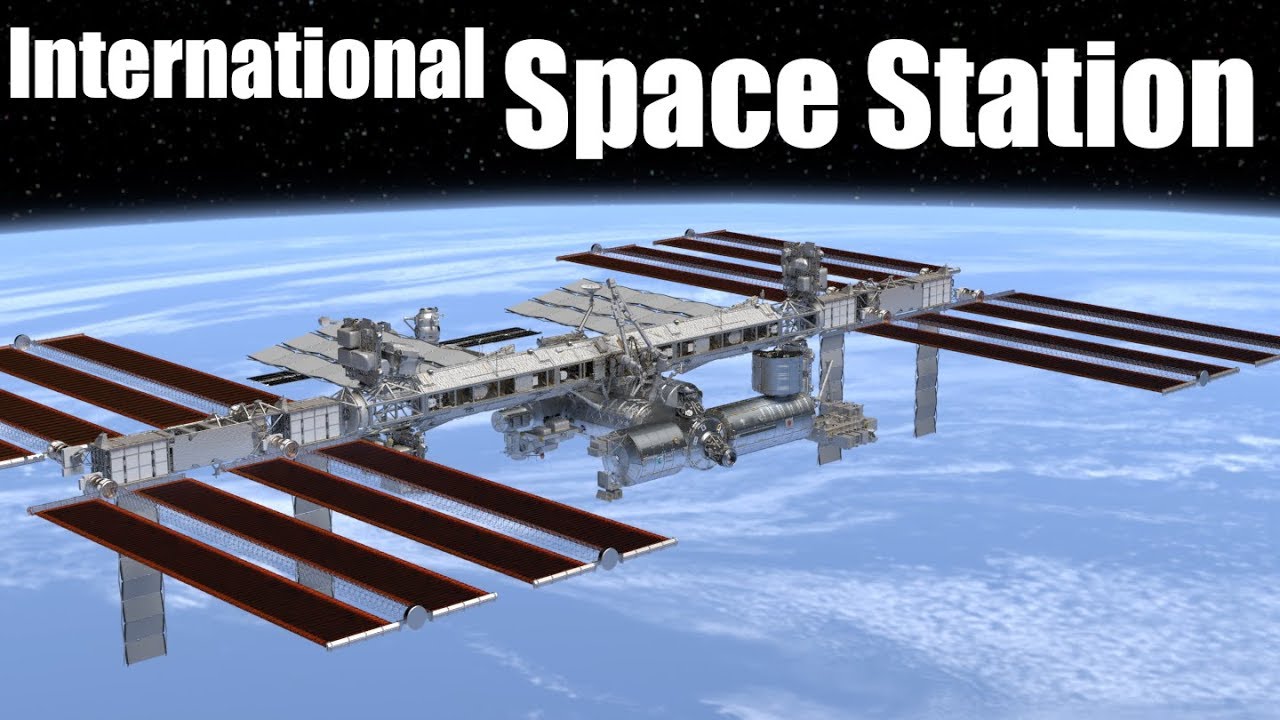
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large spacecraft that orbits Earth. It is a joint project of several space agencies, including NASA, Roscosmos, ESA, JAXA, and CSA. The ISS has been continuously occupied since 2000 and is the largest spacecraft ever built.
Purpose of the ISS
- Scientific Research: The ISS serves as a platform for conducting scientific experiments in a microgravity environment. These experiments cover a wide range of fields, including biology, medicine, physics, and astronomy.
- Technological Development: The ISS is used to develop and test new technologies for space exploration and other applications.
- Human Habitation: The ISS is a research laboratory for studying the effects of long-duration spaceflight on the human body.
Components of the ISS
The ISS is composed of multiple modules, each with a specific purpose. Some of the key components include:
- Living Quarters: The living quarters provide astronauts with a place to sleep, eat, and relax.
- Science Modules: These modules are equipped with various scientific instruments for conducting experiments.
- Power Systems: The ISS is powered by solar panels and batteries.
- Environmental Control Systems: These systems maintain a suitable environment for astronauts, including temperature, humidity, and air quality.
Life on the ISS
Astronauts living on the ISS follow a strict schedule that includes exercise, meals, and work. They also participate in a variety of scientific experiments. Despite the challenges of living in space, astronauts have reported that the experience is rewarding and fulfilling.
Future of the ISS
The ISS is expected to continue operating until at least 2030. Beyond that, there are plans to use it as a platform for commercial space activities, such as space tourism and research.
Would you like to learn more about a specific aspect of the ISS, such as its history, the experiments conducted on board, or the challenges faced by astronauts living in space?