Outer space is the region beyond Earth’s atmosphere. It is a vast and mostly empty expanse, filled with stars, planets, galaxies, and other celestial bodies.
Key Features of Outer Space
- Vacuum: Outer space is a near-perfect vacuum, meaning there is very little matter present.
- Extreme Temperatures: Temperatures in outer space can vary greatly, from the extreme cold of deep space to the intense heat near stars.
- Radiation: Outer space is filled with harmful radiation, such as cosmic rays and solar flares.
- Microgravity: Objects in space experience microgravity, meaning they appear to have no weight.
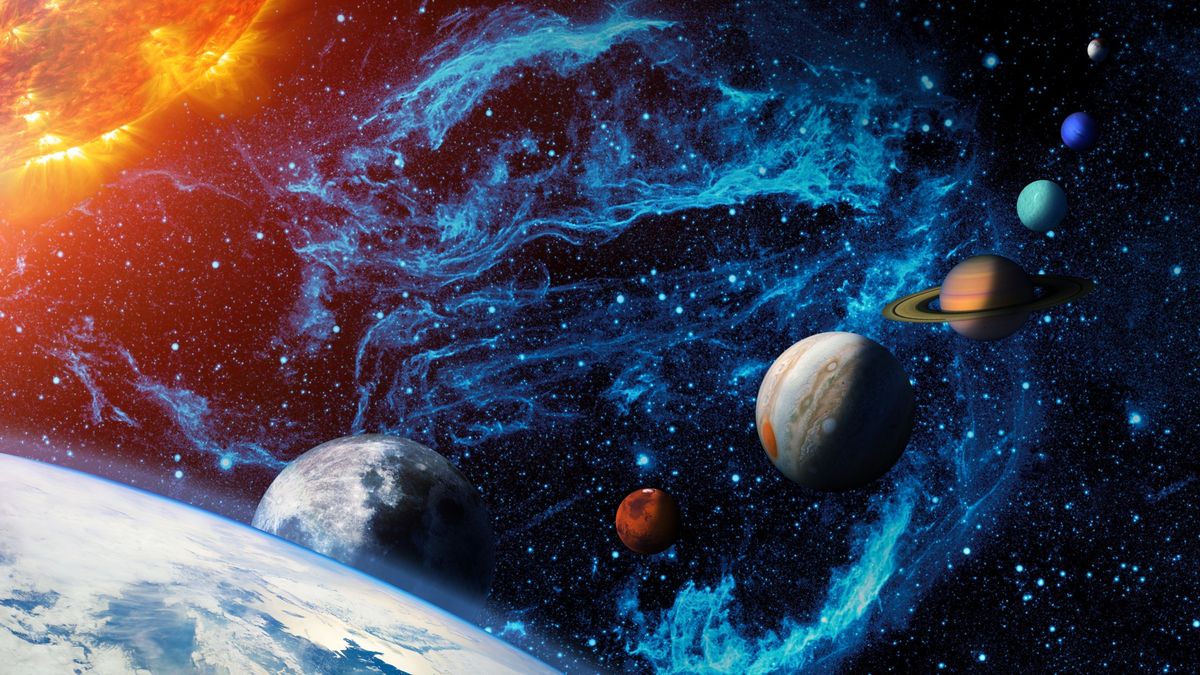
Celestial Bodies
Outer space is home to a vast array of celestial bodies, including:
- Stars: Massive spheres of plasma that generate energy through nuclear fusion.
- Planets: Celestial bodies that orbit a star.
- Moons: Natural satellites that orbit planets.
- Asteroids: Rocky objects that orbit the Sun.
- Comets: Icy bodies that orbit the Sun and have long tails when they approach it.
- Galaxies: Massive collections of stars, gas, dust, and dark matter.
Space Exploration
Humans have been exploring outer space for decades, sending spacecraft to study planets, moons, and other celestial bodies. The exploration of outer space has led to many scientific discoveries and technological advancements.
Outer space is a vast and mysterious place, and there is still much to learn about it. As we continue to explore the cosmos, we can expect to make even more groundbreaking discoveries.
Would you like to learn more about a specific aspect of outer space, such as planets, stars, or space exploration?